Modely a formáty pro grafová data - RDF a Labeled Property Graph
Vygenerováno pomocí ChatGPT na zaklade prezentaci od Klimky
RDF (Resource Description Framework)
Popis a použití:
- RDF je model grafových dat, který reprezentuje informace jako sadu trojic (subjekt, predikát, objekt). Tento model se široce používá pro sémantické modelování dat a propojení dat z různých zdrojů na webu.

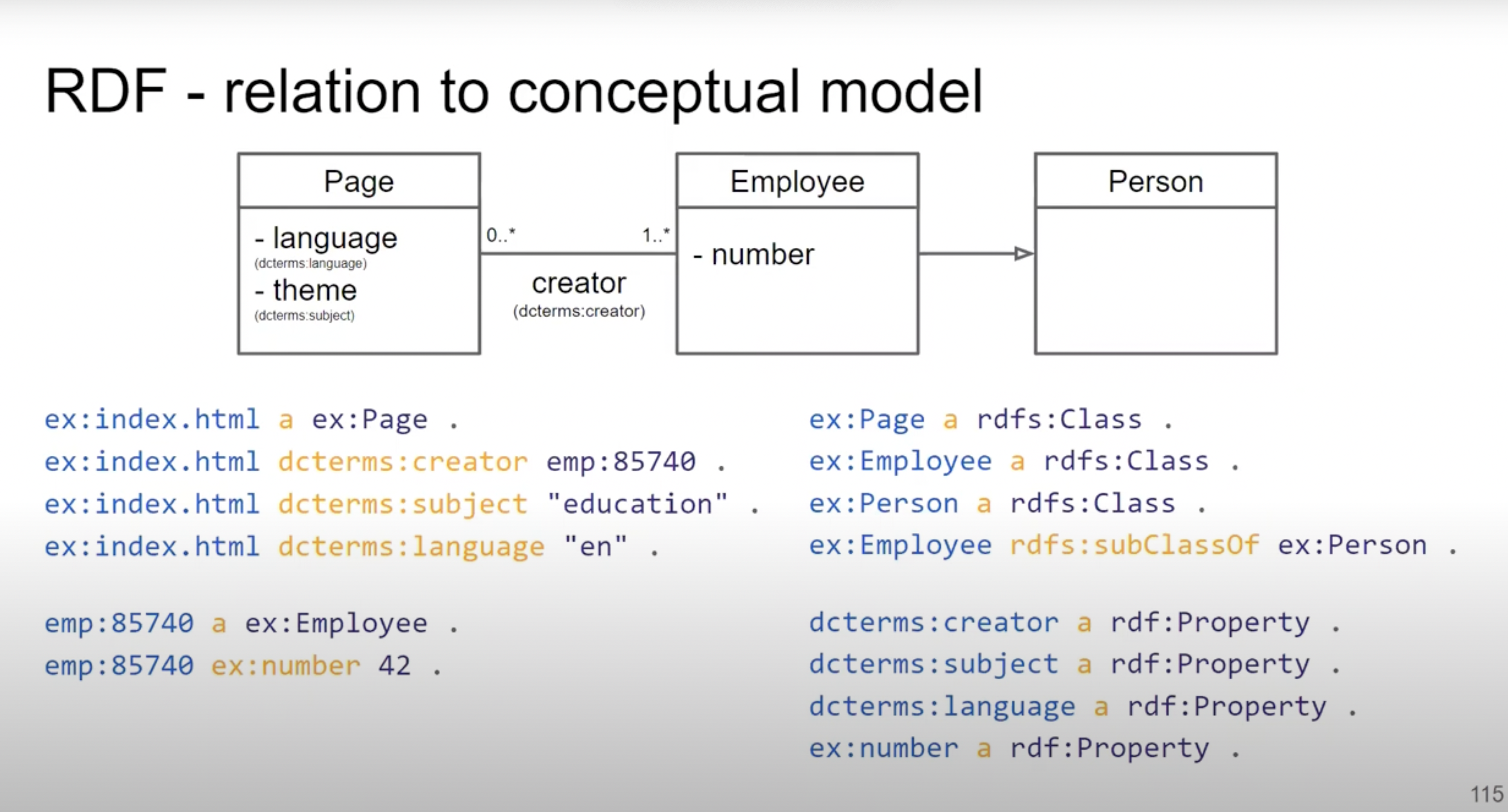
Formáty serializace dat
RDF model lze serializovat v několika formátech, z nichž každý slouží různým účelům a použitím.
1. Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language)
Turtle je lidsky čitelný formát serializace RDF, který je kompaktní a snadno pochopitelný, zejména pro ty, kteří se orientují v syntaxi RDF.



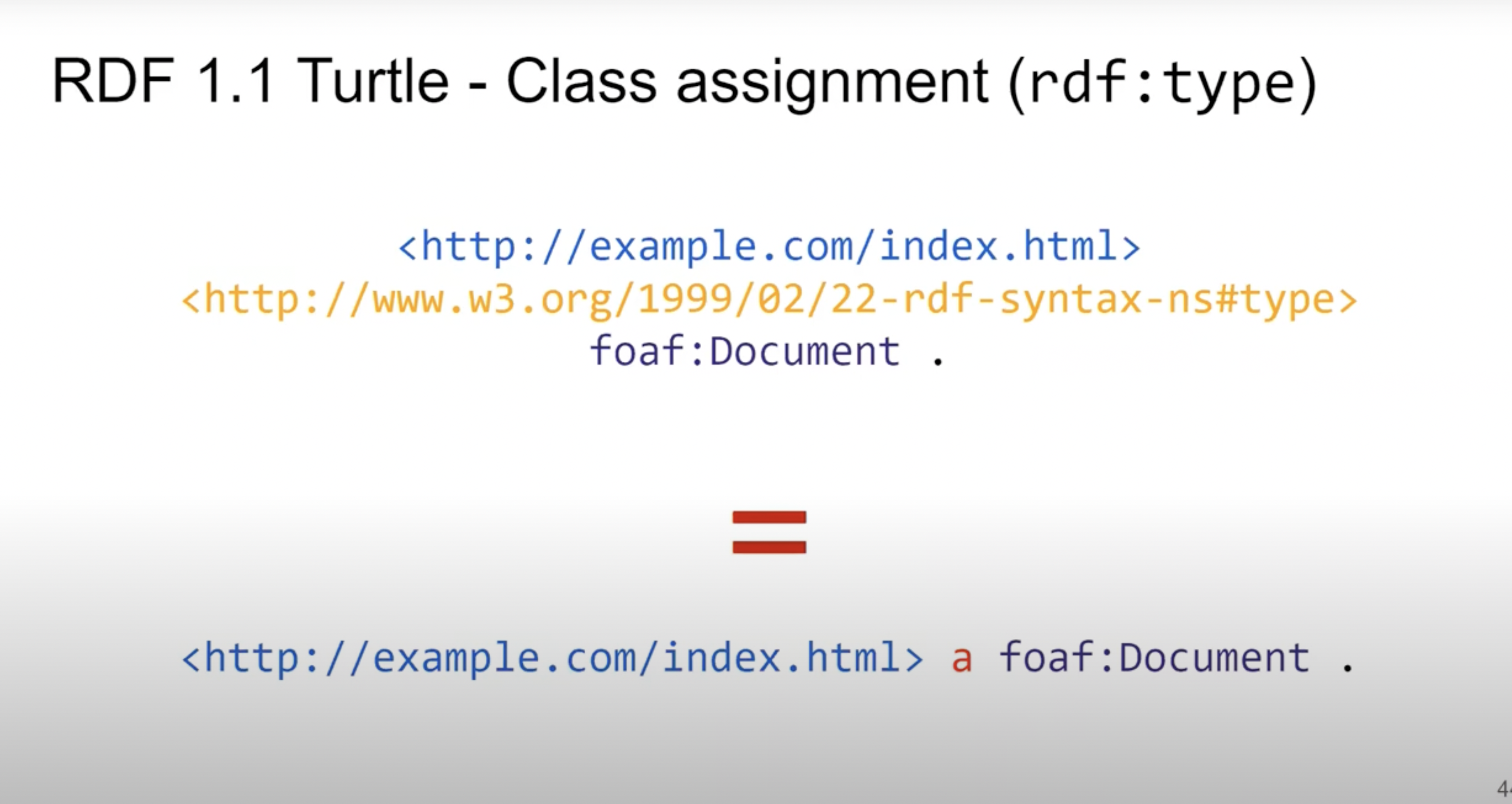

Příklad:
@prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> .
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe>
a foaf:Person ;
foaf:name "John Doe" ;
foaf:age 28 ;
foaf:knows <http://example.org/person/JaneDoe> .
2. N-Triples
N-Triples je textový formát pro kódování RDF grafů, navržený tak, aby byl jednoduchý a snadno parsovatelný.
Příklad:
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name> "John Doe" .
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/age> "28"^^<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer> .

3. TriG
TriG rozšiřuje Turtle o podporu pojmenovaných grafů, což umožňuje seskupování trojic do různých grafů v rámci jednoho dokumentu.
Příklad:
@prefix foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/> .
{
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe>
a foaf:Person ;
foaf:name "John Doe" ;
foaf:age 28 ;
foaf:knows <http://example.org/person/JaneDoe> .
}
GRAPH <http://example.org/graph1> {
<http://example.org/person/JaneDoe>
a foaf:Person ;
foaf:name "Jane Doe" ;
foaf:age 26 .
}
4. N-Quads
N-Quads je rozšíření N-Triples, které přidává podporu pojmenovaných grafů, což umožňuje přidání názvu grafu vedle subjektu, predikátu a objektu.
Příklad:
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name> "John Doe" <http://example.org/graph1> .
<http://example.org/person/JohnDoe> <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/age> "28"^^<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer> <http://example.org/graph1> .
Srovnání s Labeled Property Graph (LPG)
Popis a použití:
- RDF používá standardizovaný model, který je široce podporován na webu, a je zvláště užitečný pro propojení dat napříč různými doménami.
- LPG (Labeled Property Graph) je flexibilnější model, často používaný v grafových databázích jako Neo4j, kde uzly a hrany mohou mít vlastnosti a štítky.
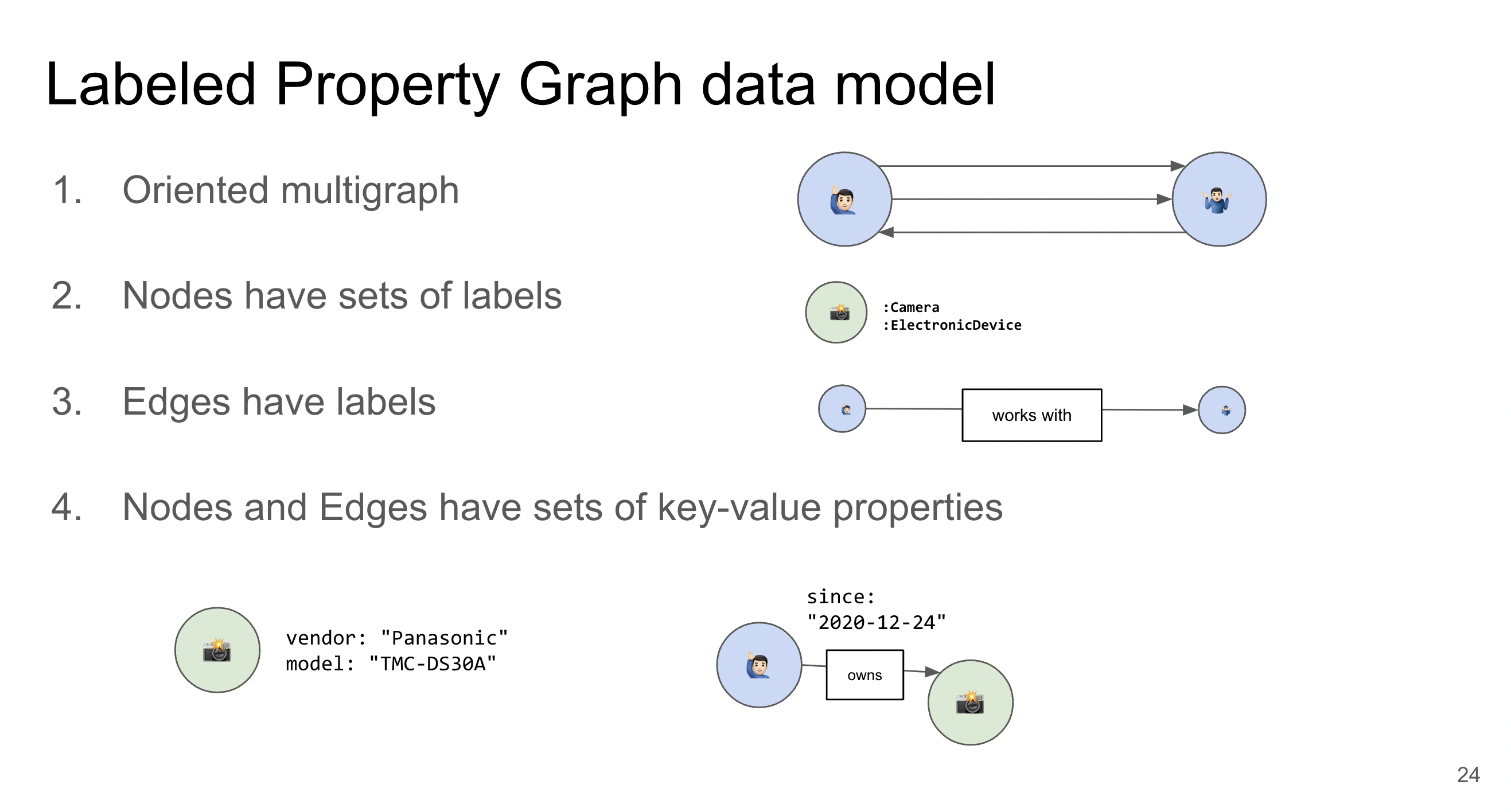
Klíčové rozdíly: - RDF je více vhodné pro aplikace, které vyžadují interoperabilitu dat a sémantickou bohatost.
- LPG je lepší pro scénáře, kde je důležitý výkon a složité dotazování v rámci jedné aplikace.
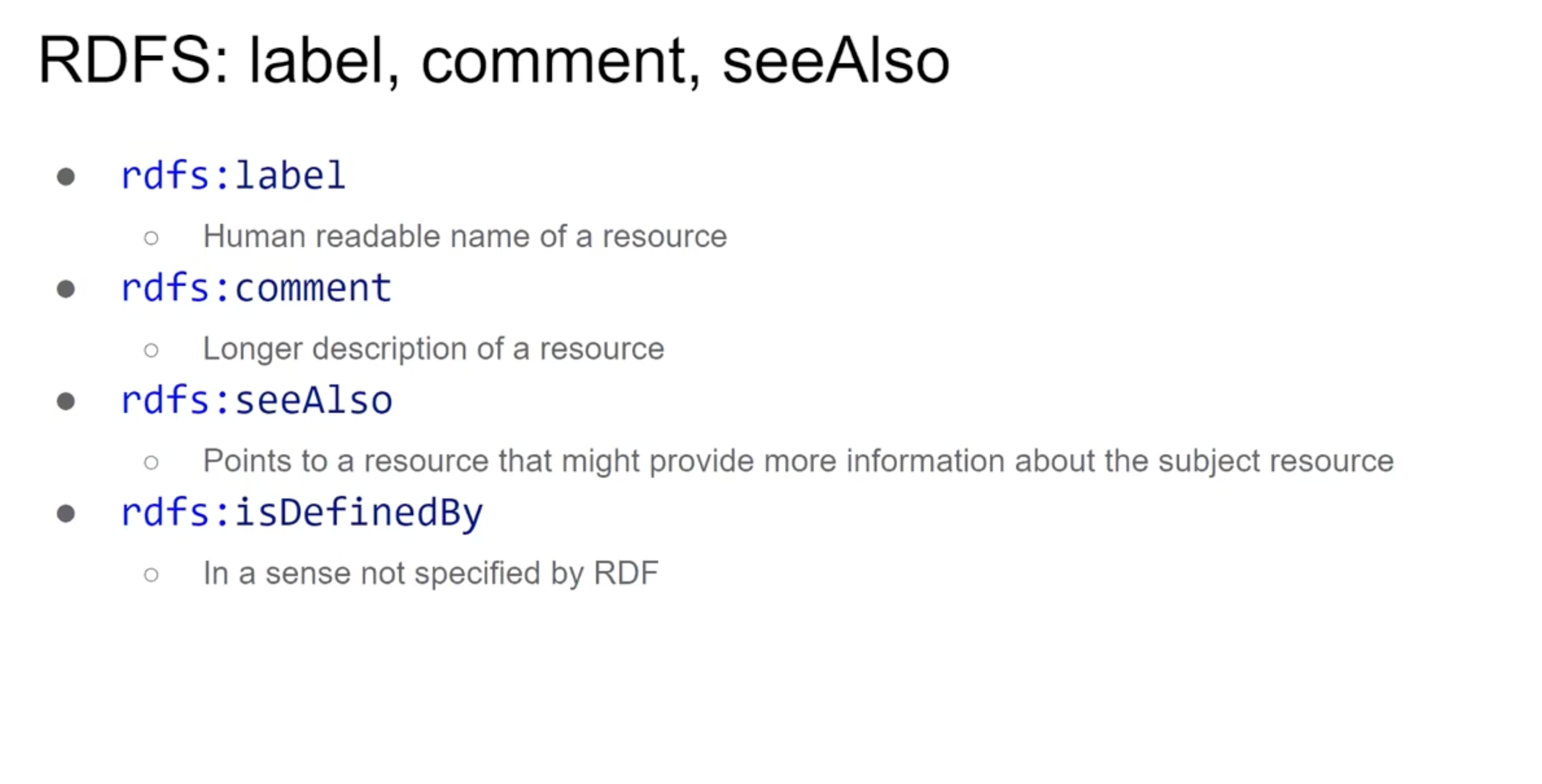
RDF Schema (RDFS)
Popis a použití:
- RDF Schema je rozšíření RDF, které umožňuje definovat třídy, vlastnosti a jejich vztahy, což usnadňuje vytvoření strukturovaných a organizovaných RDF dat.


Příklad:
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
ex:Person a rdfs:Class ;
rdfs:label "Osoba" .
ex:knows a rdf:Property ;
rdfs:domain ex:Person ;
rdfs:range ex:Person .
Dotazovací jazyky
1. SPARQL
- Transforming data in SPARQL involves querying and manipulating RDF (Resource Description Framework) data. SPARQL (SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is primarily used for querying RDF data, but you can also use it to perform some basic transformations on the data.
1. Filtering Data
- Use the
FILTERkeyword to include or exclude specific data. For example, you can filter results based on certain conditions like numerical ranges or string patterns.
SELECT ?subject ?predicate ?object
WHERE {
?subject ?predicate ?object.
FILTER (?object > 100) # Example of filtering by a numerical value
}
2. Creating New Triples
- You can create new triples (subject-predicate-object statements) using
CONSTRUCT. This allows you to transform data into a new RDF graph.
CONSTRUCT {
?subject <http://example.org/newPredicate> ?object .
}
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/oldPredicate> ?object .
}
- This query creates a new RDF triple for each result where the old predicate is replaced with a new predicate.
3. Binding Variables to New Values
- Use
BINDto create new values based on the results of expressions. This can be used to transform or calculate new data fields.
SELECT ?subject ?newValue
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/hasValue> ?value .
BIND(?value * 2 AS ?newValue) # Example of creating a new variable with transformed data
}
- In this example,
?newValueis twice the original?value.
4. Aggregation and Grouping
- SPARQL supports aggregation functions like
SUM,AVG,COUNT,GROUP_CONCAT, etc., which can be used to group and summarize data.
SELECT ?subject (SUM(?value) AS ?totalValue)
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/hasValue> ?value .
}
GROUP BY ?subject
- This query sums the values associated with each subject, grouping by the subject.
5. String Manipulations
- You can use functions like
STRLEN,SUBSTR,CONCAT, etc., to manipulate strings within your data.
SELECT ?subject (CONCAT(?firstName, " ", ?lastName) AS ?fullName)
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/firstName> ?firstName .
?subject <http://example.org/lastName> ?lastName .
}
- Here, the first and last names are concatenated into a full name.
6. Optional Data Transformation
- Use
OPTIONALto include data that might not be present for all subjects.
SELECT ?subject ?name ?optionalValue
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/hasName> ?name .
OPTIONAL { ?subject <http://example.org/optionalPredicate> ?optionalValue }
}
- The
OPTIONALkeyword allows for the inclusion of data only if it exists.
7. Transforming with Functions
- SPARQL has a variety of functions for data manipulation, such as mathematical functions (
ABS,ROUND, etc.), date functions (NOW,YEAR, etc.), and more.
SELECT ?subject (YEAR(?date) AS ?year)
WHERE {
?subject <http://example.org/hasDate> ?date .
}
- This example extracts the year from a date.
8. Combining Data from Multiple Sources
- You can use
UNIONto combine data from multiple patterns.
SELECT ?subject ?value
WHERE {
{ ?subject <http://example.org/propertyA> ?value }
UNION
{ ?subject <http://example.org/propertyB> ?value }
}
- This query combines results from two different properties into a single result set.
2. Cypher
- Cypher je dotazovací jazyk pro Labeled Property Graphs, používaný především v databázi Neo4j.
Příklad:
MATCH (p:Person)-[:KNOWS]->(friend)
RETURN p.name, friend.name